An Overview of India’s Key Initiatives to Bridge the MSME Credit Gap
India is currently one of the largest and fastest-growing economies in the world. The country’s economic growth engine—the MSME sector, has witnessed 2x growth in the last two years. That said, MSMEs face a huge credit gap of Rs. 25 Trillion, which needs to be addressed through emerging business models and digital solutions. Banks and key players in the financial services industry are introducing new payment products to reduce this gap. The FinTech sector has also stepped up and is leaving no stone unturned in offering innovative solutions that are redefining India’s digital lending landscape.

A modern and growing economy thrives against the backdrop of financial inclusion. With the rise of the working class and the rural economy showing signs of growth, India is on track to bridge the financial inclusion gap. This includes giving access to financial instruments to businesses and individuals, at reasonable rates and tailored to meet their specific needs.
In recent times, we have seen the rise of key initiatives to bridge the credit gap and tackle the issues of distribution and reach. These innovative strategies are built on digital tech and come armed with advanced data and analytics capabilities to fuel greater financial inclusion. The central and state governments in India have collaborated with financial institutions and FinTech players—and together have made concrete efforts in launching customer-acquisition strategies to enable easy access to affordable credit.
3 Key initiatives that revolutionize India’s credit landscape
An ecosystem-based approach along with trending models like embedded finance and technological interventions are employed to strengthen the foundation for the penetration of financial services in the county.
Here’s a rundown of the three most recent initiatives introduced by the Government of India to bridge the credit gap:
1 – OCEN
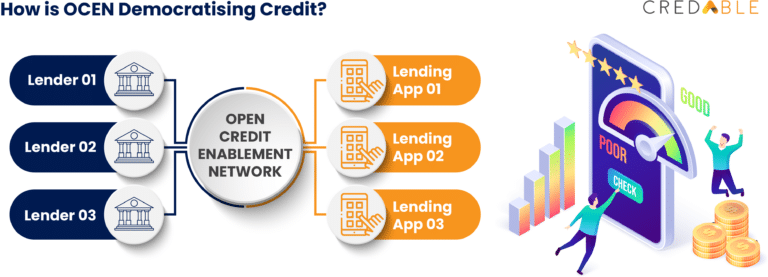
The government plans to digitize the whole lending process with the launch of the Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN). OCEN was launched in July 2020 as a part of IndiaStack—a set of open APIs that enables businesses and regulatory bodies to utilize the digital infrastructure. OCEN is a lending protocol infrastructure that provides an API framework to connect Loan Service Providers (LSPs) such as the new crop of digital lenders in the FinTech space, as well as traditional lenders like banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), with the consumers.
The core concept behind OCEN is to have a set of frameworks and protocols in place to meet the credit needs of the segments that are most vulnerable, namely the MSMEs. The flow of credit to this sector has been disrupted for years on end. Their credit requirements are very specific, often requiring small-value loans and quick access to funds. This puts a constraint on financial institutions, causing them to focus on big businesses whose credit requirements are much larger. As a result, only a meagre 11% of the 63 million MSMEs have access to formal credit.
To rectify this broken system, OCEN has an infrastructure in place that provides consent-based access to verified financial data and facilitates the sharing of verified information between all stakeholders. With OCEN, credit will become accessible to many small and medium businesses in the country like never before. CredAble is playing a key role in digitizing India’s credit ecosystem. By leveraging the OCEN technology, CredAble provides the right lender-lending product match and is paving the way towards full-fledged financial inclusion and the growth of small businesses.
2 – Account Aggregator Network
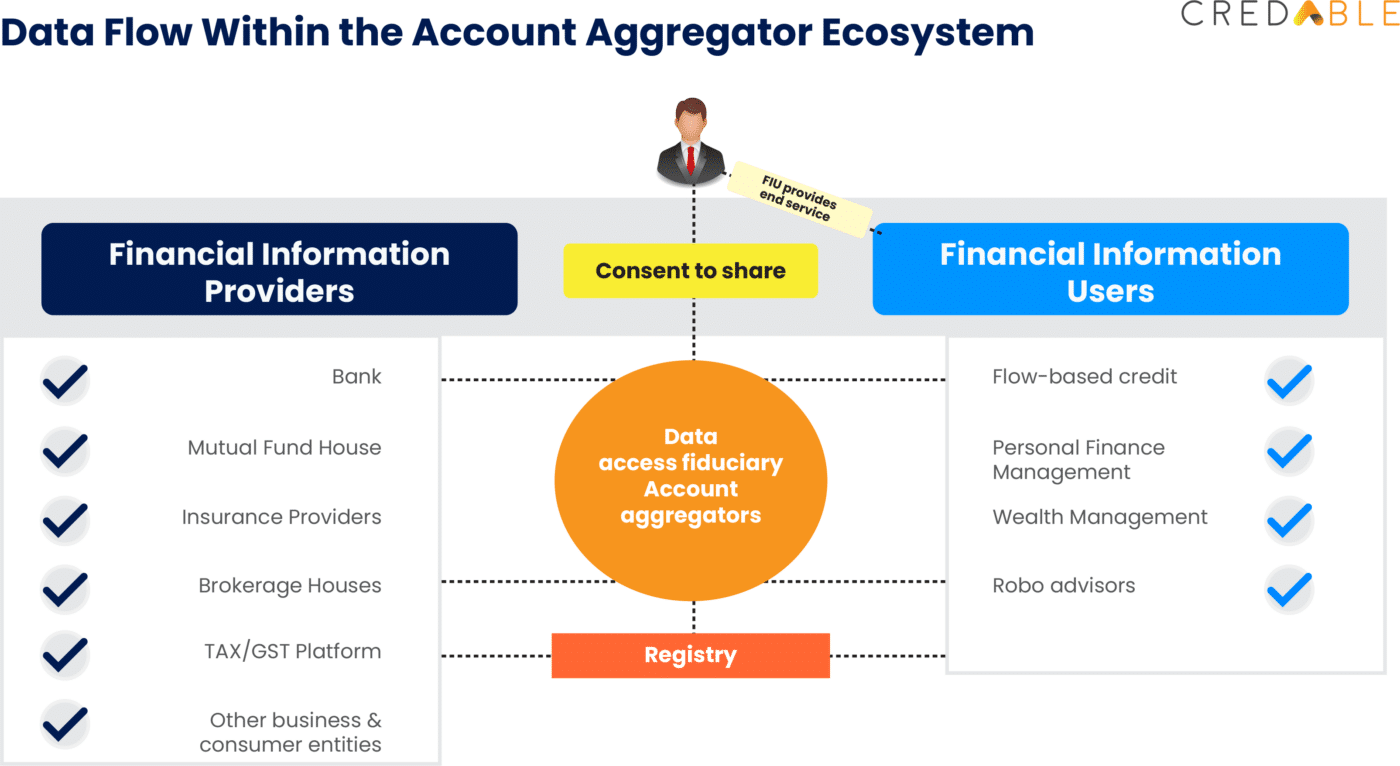
Launched by the RBI in September 2021, the Account Aggregator (AA) network is a financial data-sharing system that gives millions of individuals access to and better control of their personal financial records. An Account Aggregator is a non-banking financial company, authorized by the RBI to collect, collate and share financial information pertaining to the financial assets held by its customers.
These assets may include fixed deposits, savings deposits, current accounts, investment accounts, government securities, bonds, debentures, credit cards, loan accounts, etc. Most often the data remains in silos, AA retrieves and presents this information with the consent of the individuals, through open API connections. The Account Aggregator Network has roped in 8 of India’s leading banks on its platform to provide faster access to affordable credit. Account Aggregators take up the role of enablers and will be an important cog in the success of the OCEN-powered credit landscape.
3 – The Open Network for Digital Commerce
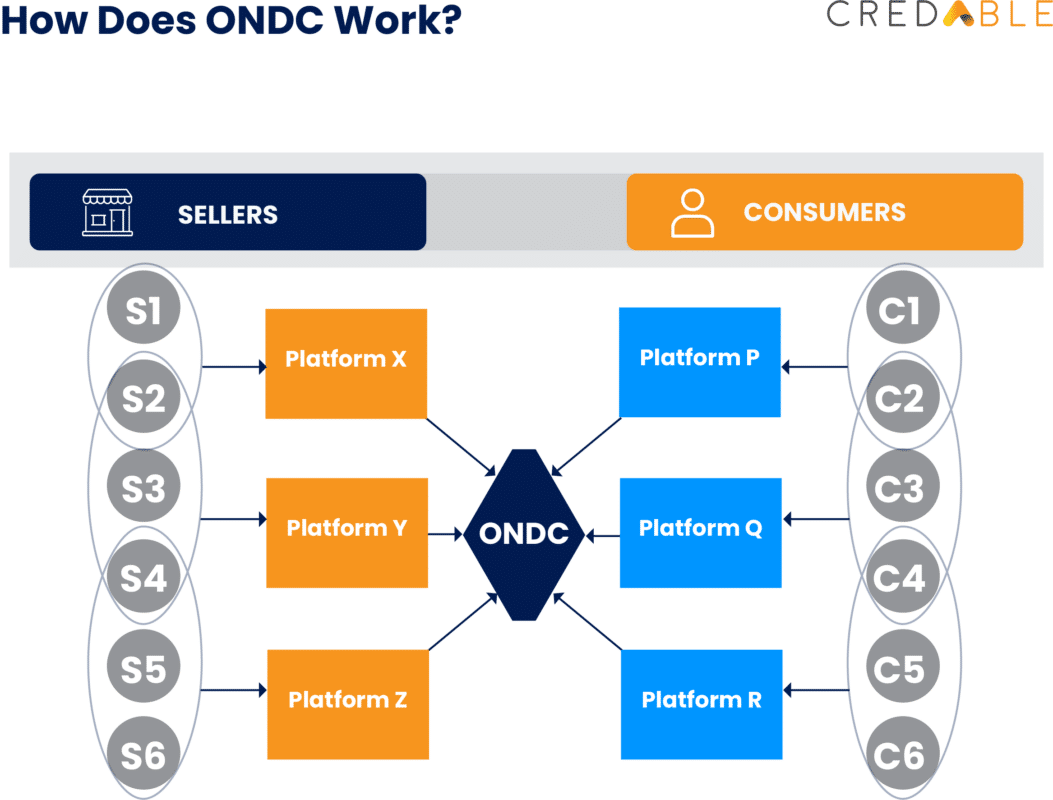
Launched in May 2022, the Open Network for Digital Commerce is a government-backed initiative intended at creating open networks for all aspects of exchanging goods and services on digital networks. The ONDC is aimed at making E-commerce more inclusive and accessible to consumers, allowing them to choose from a variety of local businesses to meet their demands.
This initiative which is currently being tested in a few cities across the country was launched by the department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade of the Government of India. Having completed 4000 successful transactions to date, the ONDC is a huge step towards democratizing the E-commerce landscape currently led by the tech giants—Amazon and Flipkart. While ONDC is accelerating the digitization of small businesses and providing a level-playing field for MSMEs, OCEN will further fortify this initiative by providing easy access to timely and affordable capital.
The next stage in India’s evolving credit and lending ecosystem
Over the years, regulatory initiatives coupled with the development of infrastructure rails such as IndiaStack have played a huge part in creating a nationwide digital ecosystem to innovate, build, and scale up a suite of financial products. While the government is geared towards introducing the underserved segments to digital financial services, key FinTech players like CredAble are building upon last-mile connectivity and are partnering with leading financial institutions to deliver low-cost and tailored products to growing businesses.
Think Working Capital… Think CredAble!
