Tokenisation: Fuelling Global Supply Chain Innovation
What is Tokenisation?
Tokenization involves issuing digital representations of assets as tokens on a blockchain. It has gained traction, with 90% of businesses using blockchain and 87% planning further investments. This process expands the investor base, breaking assets into smaller, more accessible units. Compared to traditional securities, tokenization increases liquidity and significantly reduces trading time. Projections suggest tokenized digital securities could reach $5 trillion in trade volumes within the next 7 years. The World Economic Forum notes tokenisation’s potential to bridge the gap in global trade financing and enhance SMEs' global supply chain operations.
Tokenisation and Deep-Tier Financing
Global supply chains, featuring large brands and SMEs, grapple with a $530 billion credit gap in India's $819 billion addressable demand for the MSME sector. Tokenisation's recent development has improved information and financial flow in supply chains, providing security, reducing paperwork, and enabling safer transactions. Pioneers in the industry are exploring blockchain applications in deep-tier financing.
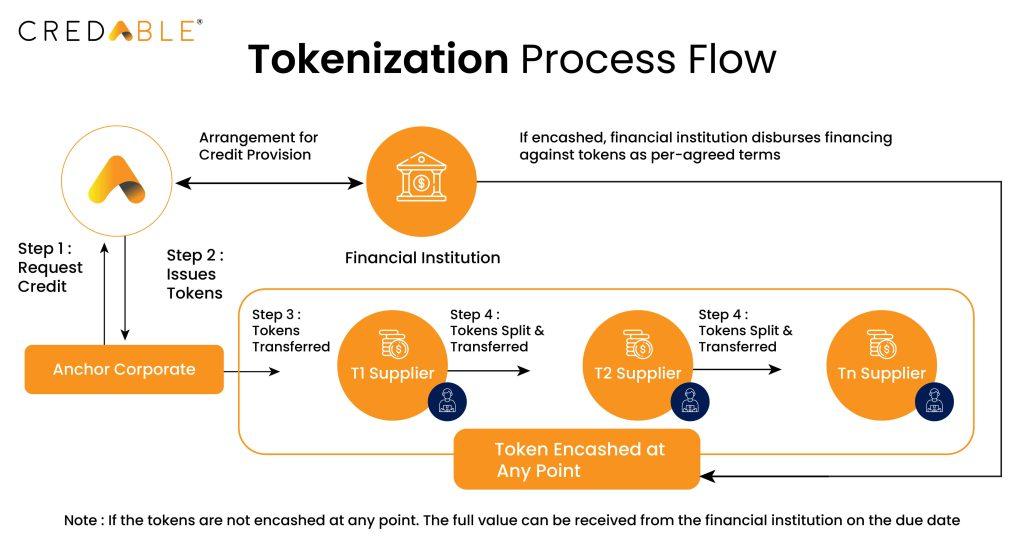
The process of tokenisation in deep-tier financing.
· In deep-tier financing through blockchain invoice tokenization, invoices from tier-1 suppliers to downstream buyers are transformed into transferable tokens.
· Each token is coded with ownership information and payment obligation details for a specific date.
· Tier-1 supplier's invoice tokens can be held until the payment due date; sold at a discounted rate for early payment; or passed up the supply chain as a form of payment.
· The same token can be transferred to tier-2 suppliers or tier-n suppliers, offering them the same options.
· This process allows payables finance to extend to deep-tier suppliers based on the anchor buyer's credit rating.
· The token's journey through the supply chain network enables affordable payables finance to be accessible for suppliers in deep tiers.
Benefits derived from blockchain financing in deep-tier financing.
Easier access to finance: The Nth suppliers gains access to finance through the tokens they receive with lower interest rates and enhanced accessibility to the required finance. In the deep-tier financing model, suppliers down the supply chain have access to secure finance and have greater availability to credit.
New sources of funding: The suppliers can tap new sources of financing once investors start to view tokens as tradable assets worth making an investment in.
Banks can broaden their customer base: Banks have the opportunity to expand their reach by tapping into new revenue streams by offering financial services to the last-mile suppliers, and at the same time gaining access to a wider range of clients.
Operational efficiency: The digitisation and automation of manual work and the reduction in a part of the reconciliation work enables the system to be more efficient. The automation of simple transaction settlements and clearance allowing fast transactions also leads to an increase in efficiency of transaction handling and optimisation in the market.
Assets fractionality: By fractionalising assets, tokenisation enables greater liquidity. The barriers to investment are cut down significantly, a wider range of people have access to buy/invest in assets. Fractioning assets also introduces the concept of shared ownership wherein multiple people can buy an asset together and use it.
Transparency: Tokenisation introduces transparency since the transactions are accessible to all the participants who are a part of the transaction. This property is inherited by all tokens representing assets.
Single source of truth: Since tokenisation uses a single layer of trust for allowing businesses or competitors to share their data, multiple participants in the ecosystem can interact with the same digital representation of an asset, driving efficiency and introducing new ways of collaboration.
Building resilience into global supply chains
CredAble’s deep-tier supply chain financing solution is enabling banking players to expand their anchor client proposition by providing supply chain financing options across multiple tiers of suppliers. CredAble is focused in integrating the method of tokenisation for the same. Tokenisation may be leveraged in deep-tier financing by freeing up liquidity from non-liquid assets such as purchase orders or unpaid invoices.
The goal of deep-tier financing is to finance the underserved suppliers at the bottom of the supply chain, leveraging blockchain technology to do the same. CredAble’s web-based model and multilevel penetration approach will enable the anchors and all their subsequent suppliers through a common framework at a lower cost. Through the deep-tier financing solution, CredAble enables its customers across their entire lifecycle to leverage the benefits of the blockchain technology, irrespective of their scale and financial strength.
Learn more on how CredAble is building resilient supply chains through deep-tier financing.
Tokenisation in the global market
The global tokenisation market is expected to grow to $5.6 billion by the year 2026, growing at a CAGR of 19% during the projected period. The market growth may be attributed to the increasing popularity of contactless payments and the continuously growing demand for cloud-based tokenisation solutions and services. The need to stay compliant with regulations and the need to ensure customer experience and maintain fraud prevention levels are also key factors in driving the tokenisation market globally. As of 2021, North America accounted for the largest share in the tokenisation market, with the Asia Pacific region expected to grow at the highest CAGR as projected in 2026. Some of the key players in the global tokenisation market include Fiserv, Visa, Mastercard, American Express, CardConnect, Micro Focus and Thales, with the majority being US-based companies and Micro Focus and Thales being UK and France-based companies respectively.
Conclusion
By integrating blockchain technology with supply chain financing, customers can benefit from the technology enhancement, more accurate credit risk assessment, various financial instrument suitable for suppliers at all tiers. This structure also streamlines working capital management through automated and more cost-
effective processes. This integration also elevates the performance of supply chain financing products and fuels the suppliers’ growth. Further, the continuous development of blockchain technology has improved the global trade standardisation and has further expanded the supply chain financing processes.
Think Working Capital… Think CredAble!
